Shop At Haya: Your Ultimate Shopping Guide
Discover the best shopping tips, trends, and deals for a smarter buying experience.
Web Accessibility: Because Everyone Deserves a Seat at the Digital Table
Unlock the digital world for all! Discover why web accessibility matters and how it ensures everyone has a seat at the online table.
Understanding Web Accessibility: Key Principles and Best Practices
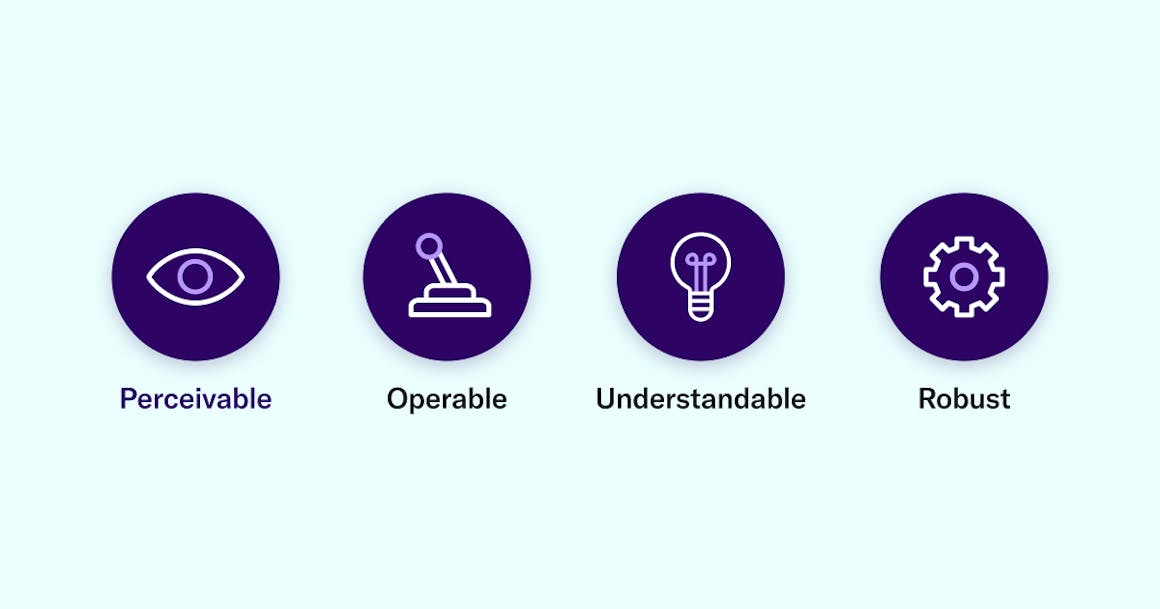
Web accessibility is the practice of designing websites and applications that everyone, including those with disabilities, can use effectively. The key principles of web accessibility are grounded in the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which emphasize the importance of making content perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust. Perceivable content means that information must be presented in ways that all users can perceive, whether through text descriptions for images or captions for videos. Operable interfaces ensure that users can navigate and interact with the web page using various tools, such as keyboard shortcuts for individuals who cannot use a mouse.
To implement best practices in web accessibility, consider the following guidelines:
- Use clear and descriptive headings to organize content.
- Ensure color contrast meets minimum standards to assist visually impaired users.
- Add alt text to images for screen readers.
- Make sure forms are labeled properly, so users understand what information is required.
- Test your website with various assistive technologies to identify potential barriers.
Top Tools and Resources for Enhancing Digital Inclusivity
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, ensuring digital inclusivity is more important than ever. To achieve this, several tools and resources can help bridge the accessibility gap. Some notable tools include:
- Screen Readers: These tools are essential for visually impaired users, converting text on screen into speech.
- Keyboard Navigation Tools: These tools allow users who cannot use a mouse to navigate content seamlessly using just their keyboard.
- Color Contrast Checkers: These help in designing websites and applications that are accessible to those with color blindness.
Besides these tools, organizations can leverage a variety of resources to foster a culture of digital inclusivity. Resources such as online training courses and community workshops can educate developers on best practices for accessibility. Moreover, employing web accessibility evaluation tools, like automated checkers, enables teams to assess and improve the inclusivity of their digital products. By integrating these tools and resources, businesses can create a more equitable and user-friendly digital experience for all.
Is Your Website Accessible? A Comprehensive Checklist for Compliance
Ensuring your website is accessible is not just a best practice; it's a legal requirement in many regions. Accessibility ensures that all users, including those with disabilities, can navigate and interact with your website effectively. This comprehensive checklist for compliance will guide you through essential elements to consider, from textual content to multimedia. Start by evaluating your website's color contrast, ensuring that it meets the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) standards to provide readability for visually impaired users.
Next, focus on the navigational aspects of your site. An accessible website should incorporate intuitive keyboard navigation, allowing users who cannot use a mouse to navigate seamlessly. Consider implementing features like alt text for images, which describe the visual content for screen readers, and ensure descriptive link text for all hyperlinks. Regularly testing your website with accessibility tools can provide insights into areas for improvement. By following this checklist, you can make significant strides towards creating a more inclusive online environment.