Shop At Haya: Your Ultimate Shopping Guide
Discover the best shopping tips, trends, and deals for a smarter buying experience.
Sugar Rush: The Sweet Truth About Diabetes
Discover the surprising link between sugar and diabetes! Uncover hidden truths and tips for a healthier life in Sugar Rush.
Understanding the Different Types of Diabetes: What You Need to Know
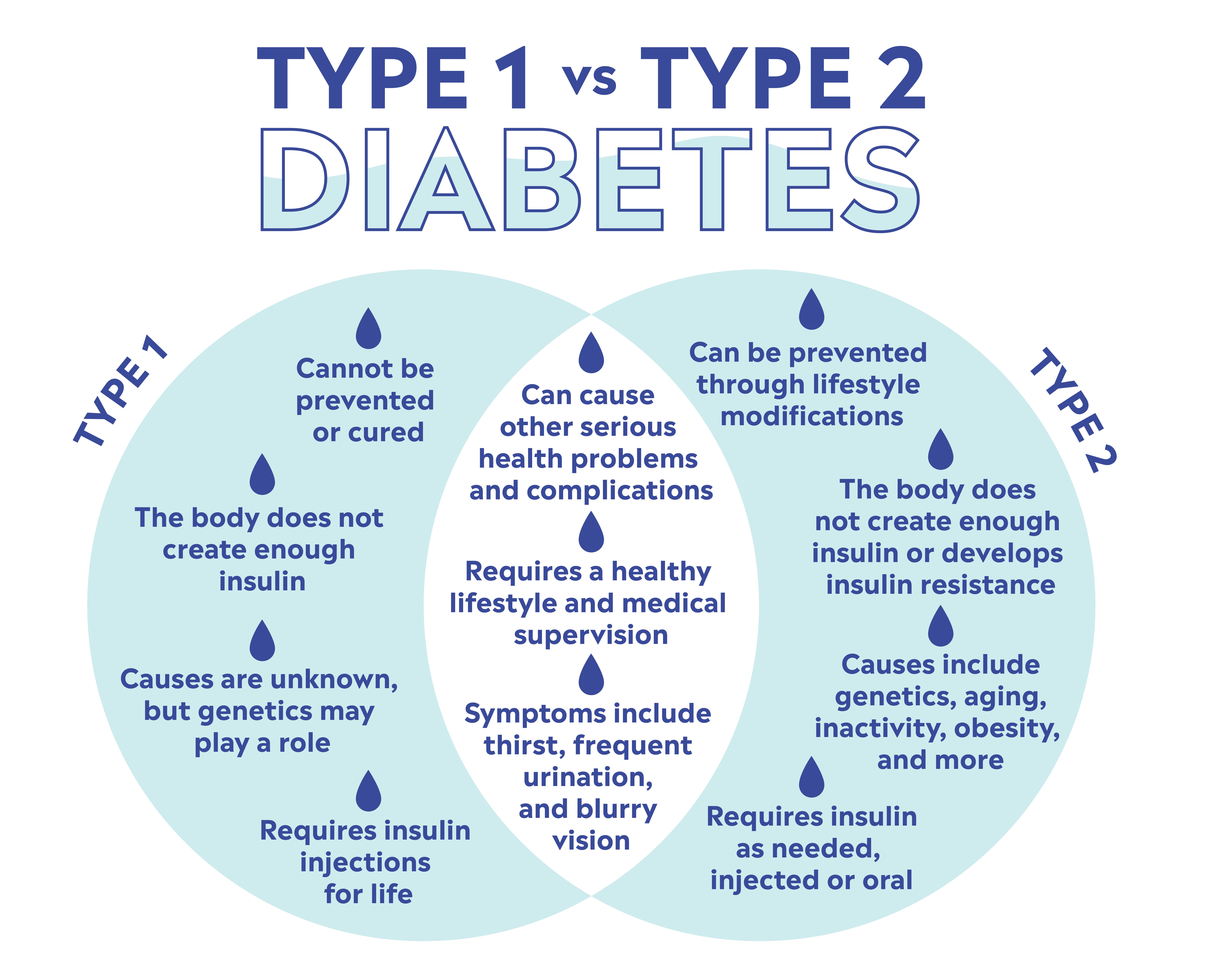
Diabetes is a complex condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, and understanding the different types is crucial for effective management. The two primary types of diabetes are Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes. Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production. This type usually develops in childhood or adolescence but can occur at any age. In contrast, Type 2 Diabetes is more common and often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and inactivity. It involves insulin resistance, where the body becomes less effective at using insulin.
In addition to these major types, there are other forms of diabetes that are important to recognize. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth, though it increases the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes later in life. Additionally, there are rare forms like Monogenic Diabetes, resulting from genetic mutations, and Secondary Diabetes, which can develop due to other medical conditions or medications. Understanding these various types of diabetes can empower individuals with the knowledge they need to manage their health effectively.
The Role of Sugar in Diabetes: Myths vs. Facts
Understanding the role of sugar in diabetes is essential for managing this chronic condition effectively. One common myth is that all sugar is harmful to people with diabetes. In reality, the body requires carbohydrates, including sugars, to function. What is critical is the type and amount of sugar consumed. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are digested more slowly and have a less dramatic effect on blood sugar levels compared to simple sugars found in sweets and sugary drinks. Therefore, it is important for individuals with diabetes to differentiate between these types of carbohydrates and focus on incorporating healthier options into their diet.
Another prevalent myth is that diabetics cannot consume any sugar at all. While managing overall carbohydrate intake is crucial, eliminating sugar completely can lead to feelings of deprivation, making it harder to stick to a healthy eating plan. Instead, people with diabetes can learn to balance their diets by moderating their sugar intake and choosing natural sources, such as fruits, that come with essential nutrients and fiber. Understanding the facts about sugar can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices that allow for the enjoyment of sweet treats in moderation, ultimately contributing to a healthier lifestyle.
How to Manage Your Sweet Tooth: Tips for Diabetics
Managing a sweet tooth can be challenging for diabetics, but with the right strategies, it is entirely possible to satisfy cravings without compromising health. One effective way to do this is by incorporating healthier alternatives into your diet. For example, consider using natural sweeteners like stevia or erythritol, which can provide the sweetness you crave without spiking blood sugar levels. Additionally, try to balance your meals with fiber-rich foods, including fruits, whole grains, and legumes, as they help keep you full and stabilize blood glucose levels.
Another helpful tip is to practice mindful eating. This means taking the time to truly enjoy and savor small portions of your favorite sweets. By paying attention to flavors and textures, you can often feel satisfied with less. Setting limits on how often and how much you indulge in sweets can also be beneficial. For instance, designate one day a week as a treat day or restrict yourself to a small serving of dessert after a healthy meal. This way, you can manage your cravings without feeling deprived, ultimately leading to a more balanced approach to a sweet tooth while maintaining a healthy lifestyle.